Optimizing Each Page
You have ensured that your site is well-indexed, so now you can focus on optimizing each page of your site. These changes apply to every page of your site, so remember to make them for every new page you create.
How to Optimize Titles and Meta Descriptions for On-Page SEO
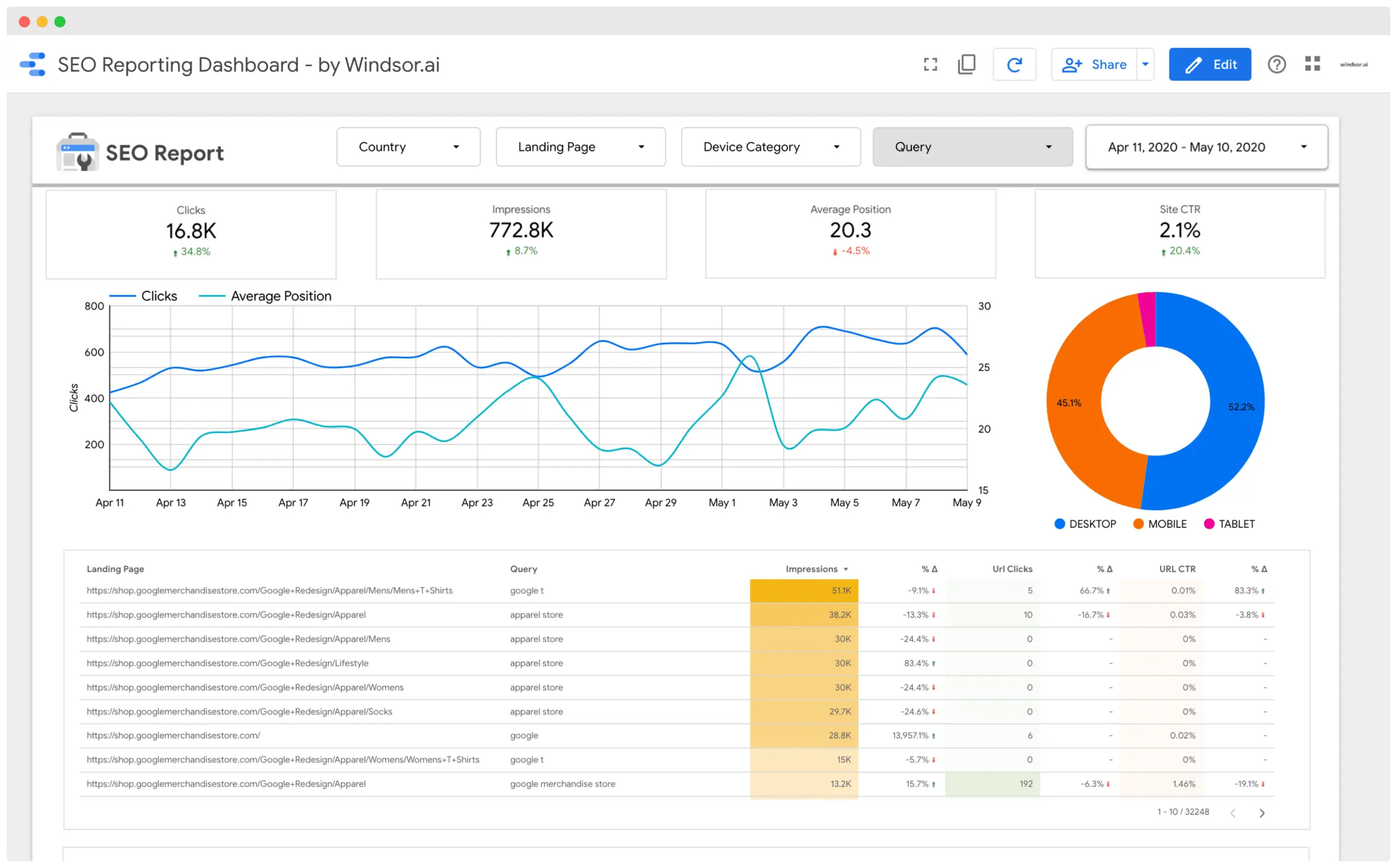
In this article, we will discuss the importance of page titles and descriptions for SEO. Look at the following example:
The above image shows a search result for "SEO.co" and as expected, our website is the first one to show up. Notice the parts of the entry that are highlighted. The headline, which contains a link, is the title tag of this page, while the brief description below it is the meta description. Title tags and meta descriptions have two main functions in SEO:
Page title tags help Google understand your content's topic. For example, a page title tag like "Why dogs bark at cars" tells Google that your page answers this question. This makes your page more relevant for a search like "why is my dog barking at cars."
Your site's appearance in search listings can make or break users' first impressions. You need to capture their attention and curiosity with a compelling start.
For all pages, your titles and descriptions should have these qualities:
1. Unique Use different titles and descriptions for each page, even if it takes more time. To find duplicate meta descriptions, go to Google Search Console (GSC) and select Search Appearance > HTML Improvements.
2. Be accurate. Use relevant keywords to describe your content as precisely as you can. However, avoid using too many keywords or repeating them unnecessarily; only use them where they fit naturally. Keyword stuffing is a bad practice.
3. Branded. Ensure your brand name follows the primary keyword phrase and page title, adopting a “Primary keyword phrase and page title | Brand name” format for most web pages.
4. Compelling. Keep in mind, the goal is to satisfy both users, by matching their search intent, and search engines alike.
To summarize, web page titles and meta descriptions have some similarities, but also some key differences. Here are the main ones:
5. Titles matter a lot. They affect how both search engines and users perceive your content, so you should optimize them as much as possible. You can be more flexible with descriptions.
6. The titles and descriptions have different length requirements. Google will cut off your material if you exceed the firm character limit. You should try to avoid this, but it's not a big deal if it happens sometimes. The limit is 75 characters for titles and 160 for descriptions.
Header tags are another important element of your web page. They are numbered from H1 to H6 and show the main topics of your content—like a summary. To help search engines understand and index your content better, you should use relevant keywords and meta data in your header tags. Meta data includes a good meta description, which is a short paragraph that describes what your page is about. Header tags have more weight than regular body text, so they can affect your ranking.